At first, I thought every PC part connected directly to the motherboard. Later, I learned some parts, like storage drives, connect through cables or other sources. This changed my perspective.
A motherboard is the main circuit board that connects and manages essential computer components. Acting as a central hub, it facilitates communication between parts but doesn’t directly connect to everything.
In this article, we explore the motherboard connects core computer parts like the CPU and RAM, managing data flow, with future trends moving toward wireless, streamlined designs.
What is a Motherboard?
The motherboard is the central circuit board in a computer, often referred to as its “heart” or “core,” as it connects and allows communication between all the system’s components.It provides a place for essential components like the CPU and RAM and offers pathways for these parts to communicate. But while it’s central, it doesn’t hold everything.
The Motherboard as a Hub
The motherboard works as a hub, connecting core components and managing data flow. But here’s the catch: not every part of your computer attaches directly to it. Some components are connected indirectly through cables, while others work via external connectors.
Core Components Connected to the Motherboard
Several essential components connect directly to the motherboard:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): This is the “brain” of the computer, directly plugged into the motherboard.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Memory modules fit into slots on the motherboard to provide quick access to data.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): While often housed in a PCIe slot on the motherboard, some GPUs are external.
- Storage Devices (SSD, HDD): These use cables or ports like SATA or M.2, often connecting directly to the motherboard.
Components That Don’t Connect Directly
Some parts, though vital, don’t connect to the motherboard:
- External Peripherals (Mouse, Keyboard, etc.): These connect via USB ports or Bluetooth, not the motherboard.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): This powers the motherboard but doesn’t plug into it directly.
- Cooling Systems: Some coolers sit on the CPU, while others connect to the case itself.
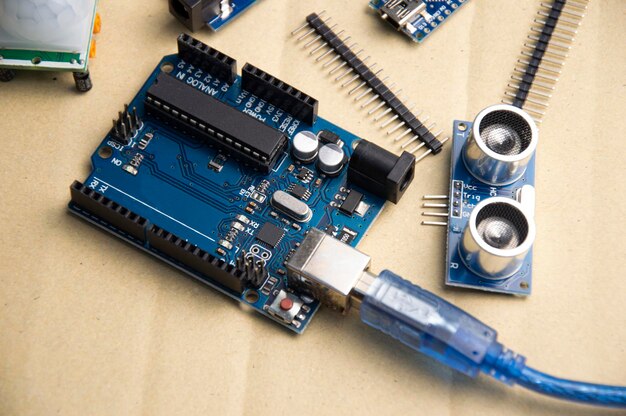
Understanding Direct vs. Indirect Connections
Motherboards have direct slots and ports, but some parts use cables to connect indirectly. Storage drives often use SATA cables, while USB hubs let multiple peripherals connect without occupying direct motherboard ports.
The Role of Expansion Slots
- PCIe Slots: Graphics cards and additional network cards connect through PCIe slots on the motherboard.
- M.2 Slots: Newer SSDs plug into M.2 slots, providing faster speeds without traditional cables.
How USB Hubs and External Connections Work
Many devices connect via USB hubs, which extend connection options beyond the motherboard’s built-in ports. These hubs are especially useful for external drives, cameras, and other devices that don’t require a direct motherboard link.
Powering the System
The PSU delivers power to all components, but it doesn’t connect directly to each one. Instead, power cables split and connect where needed, allowing components like storage drives and GPUs to receive power indirectly.
Communication Between Components
The motherboard controls the flow of data, serving as the link that connects and facilitates communication between the various components of the computer.While some parts connect directly, others communicate over data buses and circuits. This design helps reduce clutter and improve efficiency.
Modern Trends in Motherboard Connections
Today, we’re seeing more wireless connections and streamlined designs. Technologies like Wi-Fi 6E and Bluetooth reduce the need for traditional cables, showing how motherboards are adapting to changing needs.
Common Myths About Component Connections
One common myth is that the motherboard controls every component directly, but this isn’t true. Many parts, like power sources and peripherals, connect indirectly. Clearing up these myths helps build a better understanding of computer assembly.
DIY Building Tips for Beginners
When building a PC, double-check connections and follow the motherboard manual carefully. Be mindful of cable management and avoid overcrowding slots. Small mistakes, like loose connections, can cause big problems.
The Future of Motherboards and Connectivity
In the future, motherboards may evolve to support even more wireless connections and advanced power systems. These trends could reduce the need for certain cables, making computers sleeker and more efficient.
Cant connect case cables to mobo
If you’re having trouble connecting your PC case cables to the motherboard, here’s a quick guide:
Power (PWR) & Reset (RST) Buttons:
These usually go to the F_PANEL (front panel) header on the motherboard. Look for “PWR SW” and “RESET SW” labels on the cables and match them with the pins marked on the motherboard.
Power LED & HDD LED:
These light up when the PC is on or when the hard drive is active. Connect the PLED+, PLED- (Power LED), and HDD+, HDD- (HDD LED) pins to the F_PANEL too. They have polarity, so ensure the + and – are matched correctly.
USB and Audio Headers:
Connect front USB ports to the USB header and audio to the HD_AUDIO header (usually found at the bottom edge of the motherboard).
The most common motherboard problems
- No Power: The PC doesn’t turn on, possibly due to a faulty power supply, loose cables, or motherboard issues.
- Boot Failure: The computer doesn’t boot up properly, often caused by a damaged BIOS, faulty RAM, or a bad connection.
- Overheating: Poor cooling or damaged components can lead to overheating, causing the system to shut down or freeze.
- No Display: If there’s no signal on the monitor, it could be due to a faulty GPU slot, cable, or motherboard.
- USB/Peripheral Issues: Unresponsive USB ports or devices can be due to damaged ports or a motherboard failure.
- Random Crashes: Sudden shutdowns or freezes are often caused by overheating, power issues, or defective components.
Is it safe to power on a motherboard outside of its case
Yes, it’s safe to power on a motherboard outside its case for testing, as long as it’s on a non-conductive surface. Avoid static and make sure all necessary components are connected. It’s for testing, not regular use.
Why do most computer components get power through the motherboard
Components get power through the motherboard because it distributes power from the supply to the CPU, RAM, GPU, and more, simplifying connections and ensuring proper function.
Is everything in a computer connected to the motherboard?
The motherboard links nearly every part of a computer, including the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and expansion cards. However, peripherals like a keyboard, mouse, and monitor connect directly to ports on the motherboard or through additional components.
What components are attached to the motherboard?
The main components attached to the motherboard include:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the computer’s core, acting as its brain to process instructions and manage operations.
- RAM (Random Access Memory) – Temporary memory for running programs.
- Storage devices – Like SSDs or HDDs, connected via SATA or M.2 slots.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) – Often installed in a PCIe slot for video output.
- Power connectors – Are used to transfer electricity from the power supply to the various components of the computer.
- Expansion cards – Such as sound cards, network cards, or additional USB controllers.
- Cooling system – CPU coolers, case fans connected to headers.
- I/O ports – USB, audio, Ethernet ports, etc., for external connections.
How to boot a PC in safe mode?
To boot a PC in Safe Mode:
-
- Restart the PC: Click on Start > Power, then hold down the Shift key and select Restart.
- Access Advanced Options: When it restarts, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings.
- To enable Safe Mode, click Restart once more. When the Startup Settings menu shows up, press 4 or F4 to boot into Safe Mode. For Safe Mode with Networking, press 5 or F5.
After troubleshooting, restart the PC to return to normal mode.
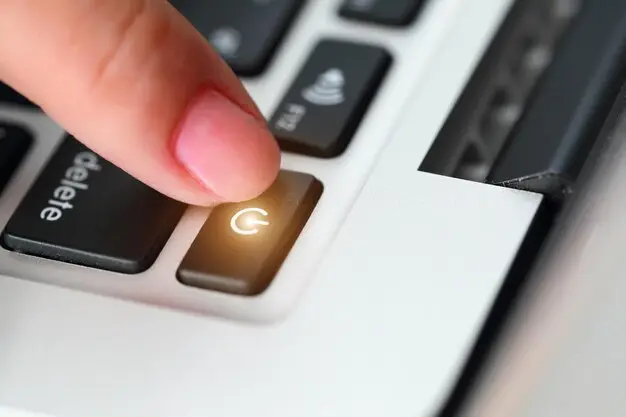

How to turn on PC without power button?
If your PC’s power button is broken, here are some ways to turn it on without using the button:
-
Use the Motherboard Power Button (if available):
Some motherboards have a built-in power button you can press.
-
-
Keyboard Power On (Wake-On-Keyboard):
- Enter the BIOS/UEFI by pressing Delete, F2, or another key specific to your PC when it starts.
- Look for a setting like Power On by Keyboard in the Power Management section and enable it.
- Save changes and exit, then use a specific key (usually space or a function key) to power on the PC.
-
Use Wake-on-LAN (for desktops):
- In BIOS/UEFI, enable Wake-on-LAN under Power Management.
- Use another device to send a “wake” signal over the network using software like Wake-on-LAN apps.
-
-
Connect Power Pins Directly (for experienced users):
-
- Open the case and locate the power switch header on the motherboard.
- Use a small metal object (e.g., a screwdriver) to briefly connect the two power pins to simulate pressing the power button.
Note: Be careful when working inside the case to avoid damage.
What part of the computer connects the monitor to the motherboard?
The video output port on the motherboard is the component that links the monitor to the computer.
If the motherboard has integrated graphics, the video output ports (like HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, or DVI) are built directly into the motherboard. The monitor is connected to one of these ports using the appropriate cable.
If the system has a dedicated graphics card (GPU), the monitor is usually connected to one of the video output ports on the GPU, which is installed into the motherboard’s PCIe slot. The GPU processes the graphics and sends the signal to the monitor.
FAQs
Can a motherboard run without GPU?
Yes, a motherboard can run without a dedicated GPU if it has integrated graphics. In that case, the CPU handles the graphical processing.
Is DisplayPort better than HDMI?
DisplayPort offers higher bandwidth and better for gaming, while HDMI is more common for TVs and home use.
Why is my computer not picking up my monitor?
Your computer might not pick up the monitor due to issues like loose cables, wrong input source, GPU or driver problems, or a faulty cable/port. Try checking connections, restarting, or testing with another cable.
Is it safe to connect a monitor to the motherboard?
Yes, it’s safe to connect a monitor to the motherboard if your CPU has integrated graphics. Otherwise, connect it to a dedicated GPU for better performance.
Can motherboard cause display issues?
Yes, a faulty motherboard can cause display issues due to damaged GPU slots, bad RAM connections, or BIOS problems. Power issues on the board can also affect display.
Conclusion
The motherboard is the central hub that connects essential components and manages data flow, though some parts connect indirectly. As technology advances, more wireless connections and streamlined designs are expected to reduce cable use and enhance efficiency.
Leave a Reply