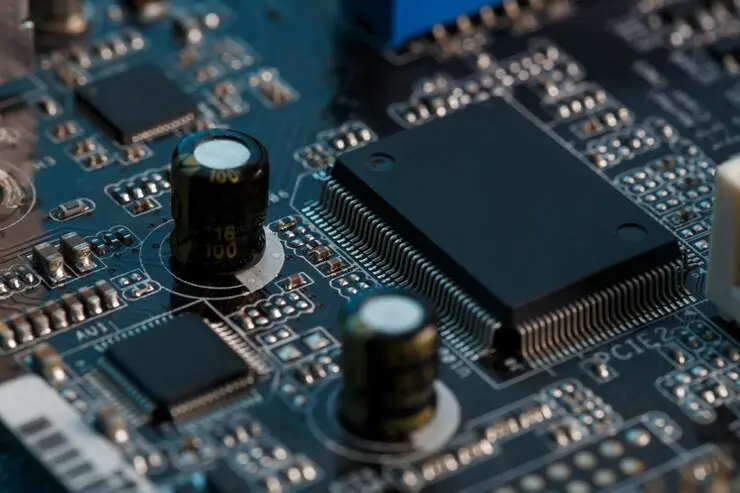
When I built my computer, I didn’t know much about the motherboard. But I learned it’s like the main hub, connecting all the parts so they work together. Without it, nothing would run. It’s the key part that helps everything in the computer communicate and function properly.
A motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer that connects and communicates between all essential components like the CPU, RAM, and storage. It allows these parts to work together, ensuring the system functions smoothly. Without it, no hardware can operate efficiently.
In this article, we will discuss the essential role of a motherboard in a computer, how it connects various components like the CPU, memory, and storage, and why it is crucial for the overall performance of your system. Let’s explore its functions and importance in detail!
What Is a Motherboard?
The motherboard is a large circuit board inside your computer that connects various hardware components, including the CPU (central processing unit), RAM (random access memory), storage devices, and more. It acts like a hub, allowing all these parts to communicate with each other so that your system functions smoothly.
How the Motherboard Works
Think of the motherboard as the central nervous system of your computer. It carries data between components, such as transferring instructions from the CPU to the memory or sending data to and from storage devices. Without a motherboard, none of these components could communicate, meaning your computer wouldn’t work.
The Role of the CPU on the Motherboard
The CPU is often called the brain of the computer, but without the motherboard to connect it to other components, it couldn’t do much. The CPU is seated on a special socket on the motherboard, where it processes data and coordinates tasks. The motherboard helps ensure that data flows smoothly between the CPU and other parts of the system.
RAM and the Motherboard
Your computer’s RAM is plugged directly into the motherboard via dedicated slots. RAM is crucial for temporarily storing data that your system is actively using, such as running programs. The motherboard manages how much RAM you can use and ensures the CPU has quick access to it for faster computing.
Storage Connections: HDD, SSD, and the Motherboard
The motherboard also connects to your storage devices, whether it’s a traditional HDD (hard disk drive) or a faster SSD (solid-state drive). These devices store all your data, from the operating system to personal files. The motherboard uses connections like SATA for HDDs and SSDs, or NVMe for even faster SSDs, to manage data flow between storage and other parts of the system.
Graphics and Expansion Cards
Your motherboard features PCIe slots, which are used to connect graphics cards (GPUs) and other expansion cards. A powerful graphics card is essential for gaming, video editing, or other graphics-intensive tasks. These slots also allow you to add other cards like sound cards or network adapters for specialized functions.
Power Distribution Through the Motherboard
The motherboard receives power from the PSU (power supply unit) and distributes it to all the components connected to it, including the CPU, RAM, and storage. It manages power flow, ensuring that each component gets the correct voltage to function properly.

Input and Output Ports on the Motherboard
Motherboards are equipped with a variety of I/O ports, such as USB, HDMI, and Ethernet ports, which allow you to connect external devices like keyboards, monitors, or the internet. These ports are essential for interacting with your system.
BIOS/UEFI: The Firmware on the Motherboard
Every motherboard has built-in software called BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). This software is crucial during the startup process, as it initializes and checks your system’s hardware before the operating system takes over.
Motherboard Form Factors
Motherboards come in different sizes, or form factors, such as ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. The form factor affects how much space the motherboard takes up inside your case and what kind of hardware it can support. Larger motherboards like ATX usually have more slots for expansion.
How the Motherboard Affects Performance
Your motherboard can impact system performance, especially if you plan to overclock your CPU or RAM for better performance. A high-quality motherboard will offer features like improved power delivery and better cooling options to ensure your system runs stably even under heavy loads.
Troubleshooting Motherboard Problems
If your system is malfunctioning, the motherboard could be to blame. Common issues include failure to boot, malfunctioning USB ports, or overheating. Diagnosing these problems can involve checking connections, updating BIOS, or even replacing the motherboard if necessary.
Motherboard Upgrades: When and Why
Upgrading your motherboard can be necessary if you’re building a new system or adding powerful components like a high-end CPU or GPU. Look for signs such as compatibility issues with new hardware or frequent system crashes to determine when it’s time for an upgrade.
How Does the Motherboard Connect to Peripherals?
The motherboard has multiple ports for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, printers, and monitors. These include USB ports, audio jacks, and HDMI/DisplayPort connections. By connecting these devices to the motherboard, it allows them to communicate with your computer and perform various tasks.
What Are Chipsets, and Why Do They Matter?
The chipset is a crucial part of the motherboard that manages data between the CPU, memory, and other peripherals. Different chipsets offer various features like overclocking support or more USB ports. Choosing the right chipset can impact system performance and future upgrade options.
Can a Motherboard Affect Gaming Performance?
Yes, the motherboard can impact gaming, especially if it has features like high-speed PCIe slots for graphics cards and support for faster RAM. A better motherboard ensures smooth data transfer, which can enhance gaming performance, especially in high-demand games.
What Are PCIe Slots Used For?
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots on the motherboard are used to connect expansion cards, like graphics cards, sound cards, or Wi-Fi adapters. They allow you to customize your computer by adding more functionality or boosting performance for specific tasks like gaming or video editing.
Do I Need to Update My Motherboard’s BIOS?
Updating your BIOS can improve system stability, fix bugs, or support newer hardware. However, it’s important to update it carefully, as an error during the update process could cause issues. Always check the motherboard manufacturer’s website for guidance on when and how to update your BIOS.
What is RAID technology?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that combines multiple hard drives to improve performance, data redundancy, or both. Common types include RAID 0 for speed, RAID 1 for data protection, and RAID 5 for a balance of both.
What is ECC memory?
ECC memory (Error-Correcting Code memory) is a type of computer RAM designed to detect and correct data corruption. It automatically corrects single-bit memory errors, which helps prevent system crashes and data corruption, making it especially useful in servers, workstations, and critical computing environments where data integrity is vital.
How do I upgrade my CPU?
To upgrade your CPU:
- Ensure the new CPU is compatible with your motherboard and BIOS.
- Power down your PC, remove the old CPU, and install the new one.
- Apply thermal paste, reattach the cooler, and power on your system.
What is overclocking?
Overclocking is when you boost the speed of your CPU or GPU beyond its normal limits, aiming for better performance than what the factory settings allow.. This enhances performance, allowing the system to run faster or handle more intensive tasks. However, overclocking can lead to higher power consumption and increased heat, which may require better cooling solutions to prevent overheating or hardware damage.
What is a CPU socket on a motherboard?
A CPU socket on a motherboard is the physical interface that connects the central processing unit (CPU) to the motherboard. It ensures the CPU is securely placed and allows communication between the processor and other components of the computer, like RAM, storage, and peripherals. Different CPU models require specific socket types, such as LGA, PGA, or BGA, depending on the CPU manufacturer and generation.
Motherboard Anatomy
A motherboard connects and communicates with all the key components of a computer. It includes the CPU socket, RAM slots, PCIe slots, chipset, power connectors, storage ports, and I/O ports. Each part serves a specific role, making the motherboard the core of the system.
Processor Socket
A processor socket (CPU socket) is a slot on the motherboard that physically connects and holds the processor (CPU). It allows the CPU to communicate with other components like memory, storage, and peripherals. Common types include LGA (used by Intel), PGA (used by AMD), and BGA (soldered directly to the board).
Internal Connectors
Internal connectors on a motherboard are vital for communication between components. Key types include:
- SATA Ports: It’s used to connect storage devices such as hard drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs).
- M.2 Slots: For high-speed NVMe SSDs.
- PCIe Slots: Allow for the addition of expansion cards, such as GPUs.
- RAM Slots: Hold the system’s memory modules (DIMM).
- Power Connectors: Supply power from the PSU to the motherboard and CPU.
- Front Panel Connectors: Link case buttons and LEDs to the motherboard.
- USB Headers: Enable additional USB ports on the case.
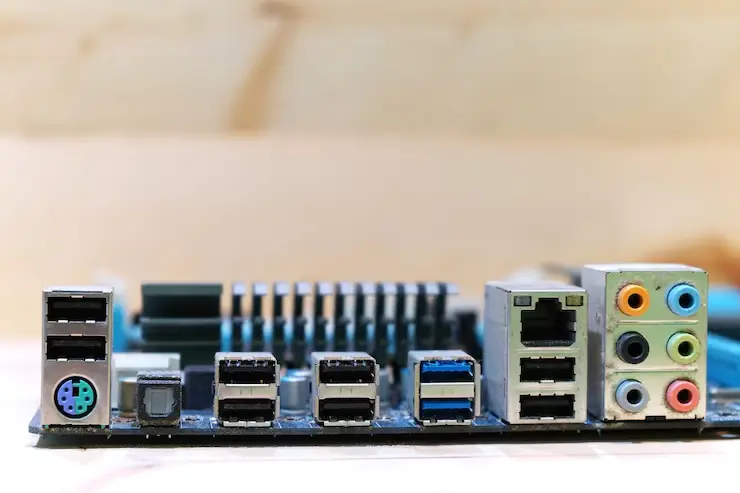
External Ports
External ports on a motherboard are critical for connecting various peripherals and devices. Key types include:
- USB Ports: Allow for the connection of external devices like keyboards, mice, and storage drives.
- HDMI/DisplayPort: Used for connecting monitors and displays to output video and audio signals.
- Ethernet Port: Provides a wired network connection for internet access.
- Audio Jacks: Connect speakers, headphones, and microphones for sound output and input.
- Thunderbolt Ports: High-speed ports for connecting devices and displays, supporting data transfer and power delivery.
What’s a PCB?
A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a flat board made of insulating material that supports and connects electronic components through conductive pathways. These boards are essential in most electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and appliances.
Key Features of PCBs:
- Layering: PCBs can be single-sided or multi-layered, allowing for complex designs and compact layouts.
- Material: Typically made from fiberglass or other insulating materials, they feature copper traces that form the electrical connections.
- Component Mounting: Components such as resistors, capacitors, and microchips are soldered onto the PCB to create functional circuits.
What Else Do Manufacturers Add?
Manufacturers often enhance PCBs by adding:
- Capacitors and Resistors: To regulate voltage and current.
- Heat Sinks: For thermal management, preventing overheating.
- Connectors: Such as USB and HDMI for easy device connections.
- Protection Circuits: Including fuses and diodes to safeguard against surges.
- Shielding: It helps reduce electromagnetic interference and enhances the quality of signals for better performance.
Do you need a motherboard in a PC?
Yes, a motherboard is essential in a PC. It serves as the main circuit board that connects all components, including the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and peripherals, enabling communication between them. Without a motherboard, the various parts of a computer cannot work together effectively.
In a computer, what is the use of the motherboard?
The motherboard is the central component of a computer, serving several key functions:
- Connectivity: It connects all major hardware components, such as the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and graphics cards, allowing them to communicate with each other.
- Power Distribution: The motherboard distributes power from the power supply unit (PSU) to the CPU, RAM, and other connected devices.
- Data Transfer: It facilitates data transfer between components through buses and chipsets, ensuring efficient operation.
- Input/Output Control: The motherboard manages input/output operations, connecting external devices like keyboards, mice, and monitors.
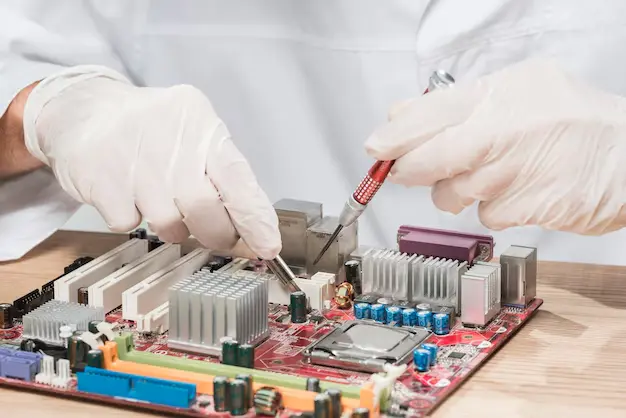
How to replace a motherboard?
Backup Data: Make sure to back up any important data to keep it safe.
Power Down: Turn off the PC and unplug it from the power source.
Open Case: Take off the side panel of your computer case to open it up.
Disconnect Components: Unplug all cables, RAM, and expansion cards from the old motherboard.
Remove Old Motherboard: Unscrew and lift out the old motherboard.
Install New Motherboard: Place the new motherboard in the case, secure it, and reconnect components.
Power On: Close the case, plug everything back in, and power on the system.
Install Drivers: Install any necessary drivers for the new motherboard.
Finding your motherboard model’s information
To identify your motherboard model, you can:
- Check System Information: On Windows, press Windows + R, type msinfo32, and look for “BaseBoard Manufacturer” and “BaseBoard Product.” Alternatively, use commands like sudo dmidecode -t baseboard on Linux.
- Physical Inspection: Open your PC case and look for the model number printed on the motherboard, usually near the CPU socket.
- Third-Party Software: Utilize programs like CPU-Z or Speccy for detailed information about your motherboard.
Caring for the motherboard
To ensure your motherboard lasts longer and functions effectively, consider these tips:
- Keep It Clean: Regularly clean dust from the motherboard using compressed air to prevent overheating.
- Monitor Temperature: Ensure proper airflow in your PC case to avoid overheating. Consider adding extra fans if necessary.
- Secure Connections: Check that all cables and components are securely connected to avoid malfunctions.
- Prevent Static Damage: Ground yourself when handling the motherboard to prevent static discharge damage.
- Update BIOS: Keep your BIOS and drivers up to date to enhance performance and compatibility.
Can you explain the role of the motherboard in a computer system unit?
The motherboard is the central circuit board that connects all parts of a computer system.. It connects the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and peripherals, allowing them to communicate and work together. It also distributes power to these components and manages data transfer between them.
FAQs
What is the main function of a motherboard?
The motherboard connects and allows communication between all the key components in a computer, such as the CPU, RAM, and storage.
How does a motherboard impact computer performance?
The quality of your motherboard can affect things like overclocking and overall stability, especially when using high-end components.
Can I upgrade just the motherboard in my computer?
Yes, but you’ll need to ensure compatibility with your CPU, RAM, and other components before upgrading.
What happens if my motherboard fails?
If the motherboard fails, your system will likely not boot or function properly. You may need to replace it if repairs aren’t possible.
What’s the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
BIOS is older firmware, while UEFI is newer and offers more features, faster boot times, and support for larger hard drives.
What is the main purpose of a motherboard?
The main purpose of a motherboard is to connect and allow communication between all the computer’s components, including the CPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals. It also distributes power to these parts and manages data flow.
Does a motherboard affect FPS?
A motherboard can affect FPS (frames per second) indirectly. While it doesn’t directly impact gaming performance, it influences how efficiently components like the CPU, GPU, and RAM communicate. A high-quality motherboard with good power delivery, support for faster RAM, and optimal PCIe slots can ensure better overall performance, potentially leading to more stable or higher FPS.
Do I need a motherboard for my PC?
Yes, a motherboard is essential for your PC. It serves as the main circuit board, connecting all the components like the CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage. Without it, these parts can’t communicate or function together.
What does a motherboard do for gaming?
A motherboard plays a key role in gaming by connecting and managing all critical components like the CPU, GPU, and RAM. It affects system stability, component communication, and upgrade potential. A high-quality motherboard supports overclocking, faster RAM speeds, and better connectivity options, which can enhance gaming performance and smoothness, especially in demanding games.
What does a CPU do?
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of a computer. It performs all the instructions from software by processing data, executing calculations, and managing tasks. The CPU handles everything from running programs to controlling peripheral devices, making it essential for system performance.
Motherboard components?
A motherboard includes key components like the CPU socket (for the processor), RAM slots (for memory), and PCIe slots (for graphics and other expansion cards). It also has power connectors, chipsets, and storage connectors like SATA and M.2.
What does RAM do?
RAM (Random Access Memory) temporarily stores data that your computer needs to access quickly. It allows the CPU to quickly retrieve data, making programs and tasks run faster. More RAM improves multitasking and system performance by reducing the need to fetch data from slower storage drives.
Conclusion
The motherboard plays a central role in making your computer work by connecting all of its parts. Whether you’re a casual user or a gaming enthusiast, understanding how your motherboard functions will help you make better choices when building or upgrading your system.